Posted by Sagé de Clerck, IMF Statistics Department
 The IMF has prepared a Fact Sheet describing what is involved in compiling government finance statistics (GFS), and how these data relate to the fiscal cycle, source data, and accounting systems. GFS are key to economic analysis and also a major input for national accounts statistics. GFS facilitate consistency with other macroeconomic datasets and enhance international comparability.
The IMF has prepared a Fact Sheet describing what is involved in compiling government finance statistics (GFS), and how these data relate to the fiscal cycle, source data, and accounting systems. GFS are key to economic analysis and also a major input for national accounts statistics. GFS facilitate consistency with other macroeconomic datasets and enhance international comparability.
Data users are often faced with a myriad of fiscal data: from the budget process, from various specialized budget reports, or from audit reports, and users can easily get lost in the data labyrinth. The Fact Sheet will help users of fiscal data better understand these differences. Compilers of GFS will also find it helpful to understand differences among these various datasets and how they relate to each other. Where necessary, GFS compilers should publish reconciliations of the data to instill confidence in the reliability of the data.
Frequently asked questions from users suggest a need to clarify the different types of data and their applications. For example, “central government budget data” are used in policy decisions at a national level while “budget execution reports” are useful to monitor progress with implementing these decisions. In contrast, to capture governments' involvement in the production and growth of the economy, as measured in the national accounts, a more comprehensive measure covering the "general government" is required.
The Fact Sheet is designed as a nontechnical document to inform policy makers and data users. It introduces the terminology, processes, and common challenges in preparing these data. It provides a synopsis of the international standard, the Government Finance Statistics Manual 2001 (GFSM 2001) tailored on the model of commercial accounting. The GFSM2001 is consistent with the terms and concepts of other international statistical standards such as the 1993 System of National Accounts (1993 SNA).
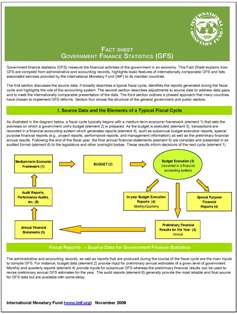
A diagram in the Fact Sheet illustrates the links between compilation of government finance data and the fiscal policy cycle. A generic map of the structure of government is included to emphasize that published data should always be specific about the institutional coverage, for instance whether the data cover central government, general government, or the entire public sector. Similarly, the basis of recording (e.g., cash basis or a noncash basis, such as accruals) should be disclosed. A chart describes typical roadmaps followed by many countries to develop their fiscal statistics, including sovereign balance sheets to supplement data on the government's debt and their links to public accounting systems.
The Statistics Department of the IMF collects annual GFS data for about 120 member countries and disseminates (electronically) Government Finance Statistics Yearbook (GFSY) data using the GFSM 2001 presentation. In addition, quarterly and monthly data are currently collected for about 80 countries. These are published in the International Financial Statistics (IFS). Both are available for a fee on the IMF's External website.
The Factsheet is available below in Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish.
Download GFS Fact Sheet (ARABIC)
Download GFS Fact Sheet (CHINESE)
Download GFS Fact Sheet (ENGLISH)
Download GFS Fact Sheet (FRENCH)